[Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan Vol.18, 142-144, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> ペロブスカイト太陽電池材料におけるポーラロン形成の量子力学的分子動力学シミュレーション
<Author(s):> 浦谷 浩輝, 周 建斌, 中井 浩巳
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> nakai(at)waseda.jp
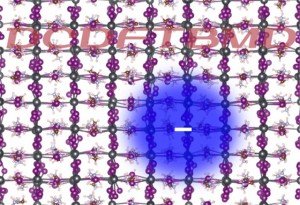
<Abstract:> Polarons, which are charge carriers in solids wearing a structural deformation, play a key role in photo-electronic devices such as solar cells. In this study, the polaron formation process in a lead halide perovskite, which is utilized in perovskite solar cells, was simulated using quantum mechanical molecular dynamics calculations. The simulations were performed in a several nanometers-scale model system to capture the spatial size of the polarons, with the use of the divide-and-conquer type density-functional tight-binding method, which is capable of fully quantum mechanical treatment of systems consisting of (tens of) thousands of atoms. The observed structural deformations and their process are discussed.
<Keywords:> Polaron, Perovskite solar cell, Divide-and-conquer method, Density-functional tight-binding method, Quantum mechanical molecular dynamics simulation
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/18/3/18_2019-0025/_article/-char/ja/