[Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan Vol.24, 36-38, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> Givens回転と誤差逆伝播法を組み合わせた自己無撞着場計算の高効率収束法の開発
<Author(s):> 大島 玲生, 中井 浩巳
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> nakai(at)waseda.jp
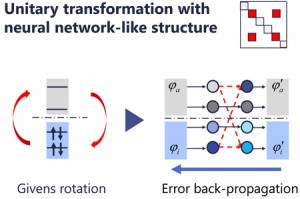
<Abstract:> We have recently proposed a highly efficient convergence method for self-consistent (SCF) calculations combining Givens rotation and error back-propagation (EBP) algorithms, referred to as direct Givens rotation (DGR) method [J. Chem. Phys. 162, 014108 (2025)]. The Givens rotation corresponds to unitary transformations that guarantee the orthogonality of molecular orbitals. Complicated gradients constructed through sequential Givens rotations were computed using the EBP technique without deriving explicit forms. This article reviews the proposed DGR method and compares it with conventional methods such as the standard SCF procedure, the second-order SCF method, and the direct inversion in iterative subspace technique for H2O molecule. The DGR method exhibited a convergence speed comparable to that of the SOSCF method while achieving a lower and more reliable energy.
<Keywords:> キーワード self-consistent field, direct minimization, Givens rotation, error back-propagation, Hartree-Fock, Kohn-Sham density functional theory
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/24/1/24_2025-0003/_article/-char/ja/
<Title:> Givens回転と誤差逆伝播法を組み合わせた自己無撞着場計算の高効率収束法の開発
<Author(s):> 大島 玲生, 中井 浩巳
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> nakai(at)waseda.jp
<Abstract:> We have recently proposed a highly efficient convergence method for self-consistent (SCF) calculations combining Givens rotation and error back-propagation (EBP) algorithms, referred to as direct Givens rotation (DGR) method [J. Chem. Phys. 162, 014108 (2025)]. The Givens rotation corresponds to unitary transformations that guarantee the orthogonality of molecular orbitals. Complicated gradients constructed through sequential Givens rotations were computed using the EBP technique without deriving explicit forms. This article reviews the proposed DGR method and compares it with conventional methods such as the standard SCF procedure, the second-order SCF method, and the direct inversion in iterative subspace technique for H2O molecule. The DGR method exhibited a convergence speed comparable to that of the SOSCF method while achieving a lower and more reliable energy.
<Keywords:> キーワード self-consistent field, direct minimization, Givens rotation, error back-propagation, Hartree-Fock, Kohn-Sham density functional theory
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/24/1/24_2025-0003/_article/-char/ja/