[Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan Vol.24, 95-98, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> Development of Machine Learning Models to Reproduce Coupled-Cluster Molecular Energies
<Author(s):> Taichi SOMEGO, Yasuhiro IKABATA, Hitoshi GOTO
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> gotoh(at)tut.jp
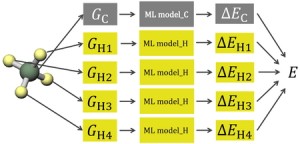
<Abstract:> We attempted to reproduce molecular energies at the coupled-cluster level from molecular structures by constructing machine learning models that reproduce atomic environment energies, defined as the difference between the atomic energy in a molecule and that of the corresponding isolated atom. To obtain atomic energies from quantum chemical calculations, we adopted energy density analysis. Our results showed that the prediction accuracy of coupled-cluster molecular energies was comparable to that for density functional theory.
<Keywords:> Coupled-cluster method, Molecular energy, Machine learning, Energy density analysis, Atomic environment energy
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/24/3/24_2025-0014/_article/-char/ja/
<Title:> Development of Machine Learning Models to Reproduce Coupled-Cluster Molecular Energies
<Author(s):> Taichi SOMEGO, Yasuhiro IKABATA, Hitoshi GOTO
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> gotoh(at)tut.jp
<Abstract:> We attempted to reproduce molecular energies at the coupled-cluster level from molecular structures by constructing machine learning models that reproduce atomic environment energies, defined as the difference between the atomic energy in a molecule and that of the corresponding isolated atom. To obtain atomic energies from quantum chemical calculations, we adopted energy density analysis. Our results showed that the prediction accuracy of coupled-cluster molecular energies was comparable to that for density functional theory.
<Keywords:> Coupled-cluster method, Molecular energy, Machine learning, Energy density analysis, Atomic environment energy
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/24/3/24_2025-0014/_article/-char/ja/