[Advanced Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> Electronic Origin of Catalytic Nitric Oxide Reduction upon Small Rhodium and Copper Clusters
<Author(s):> Ryoichi FUKUDA
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> fukuda(at)esicb.kyoto-u.ac.jp
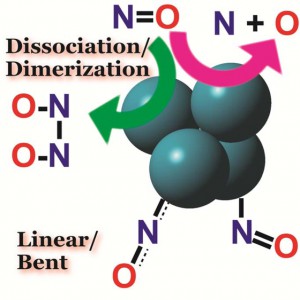
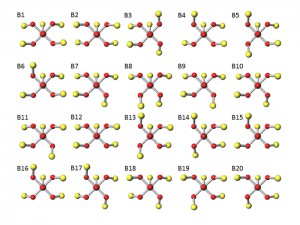
<Abstract:> Both rhodium and copper show a catalytic activity for nitric oxide (NO) reduction; however, the reaction mechanisms can be different. Herein, we elucidate the difference in the NO reduction mechanisms between Rh and Cu clusters regarding the electronic structures using DFT computations and small cluster models involving four metal atoms. The computational results show that the dissociative adsorption proceeds on the Rh cluster with the reaction barrier of 33 kcal mol-1. The calculated heat of the reaction is almost zero. On the Cu cluster, the calculated reaction barrier reaches to 78 kcal mol-1 indicating that the dissociative adsorption hardly occurs. Instead of the dissociative adsorption, dimerization of NO initiates the catalytic NO reduction on Cu cluster. The calculated energy barrier for the dimerization is 8 kcal mol-1. The adsorbed NO dimer has a similar stability to co-adsorbed two NO molecules. In contrast, the dimerization hardly occurs on the Rh cluster; the reaction pathway is remarkably endothermic, and a stable adsorbed product is not found. The adsorption structures of NO can explain such differences. On Cu cluster, NO takes bent-nitrosyl conformation that acts as an electron acceptor. On Rh cluster, NO acts as an electron donor having linear-nitrosyl conformation.
<Keywords:> Nitric oxide reduction, Catalytic reaction mechanism, Chemical bond, Transition metal cluster
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/advpub/0/advpub_2018-0037/_article/-char/ja/