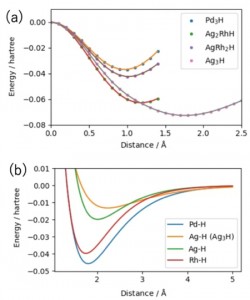
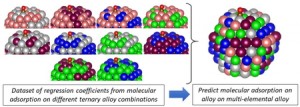
[Advanced Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> 化学勾配に駆動される膜興奮動態による単細胞生物ゾウリムシの障害物衝突に対する行動応答モデル
<Author(s):> 大嶺 志歩, 國田 樹
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> kunita(at)ie.u-ryukyu
<Abstract:> 本研究は,生物の柔軟な行動を生み出す情報処理システムの本質的原理を化学勾配に基づく数理モデルで表現することを目的とした.単細胞生物の繊毛虫ゾウリムシが障害物に衝突した際の行動応答を生物実験により調べた結果,ゾウリムシは衝突後すぐに方向転換する行動と,障害物に沿って移動した後に方向転換する行動を示した.これらの行動を生じた時の衝突時の角度や速度は同じであったが,直前の角度変化の符号が異なっていた.ゾウリムシの行動は,体表に生えた繊毛運動によって制御され,それは細胞内外の化学勾配に従って生じる膜興奮動態によって調整される.この膜興奮動態と行動とを対応づける数理モデルを構成し,数値シミュレーション実験を行った.その結果,実験結果と同様にゾウリムシが障害物に衝突する前の角度変化の符号の違いで2つの行動を再現できた.つまり,ゾウリムシは同じ化学勾配状態でも,直前の角度変化という運動履歴の違いによって異なる行動を生じる柔軟性を有していた.
<Keywords:> membrane excitation dynamics, chemical gradients, Paramecium, ciliary movement, FitzHugh-Nagumo model
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/advpub/0/advpub_2024-0026/_article/-char/ja/
<Title:> 化学勾配に駆動される膜興奮動態による単細胞生物ゾウリムシの障害物衝突に対する行動応答モデル
<Author(s):> 大嶺 志歩, 國田 樹
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> kunita(at)ie.u-ryukyu
<Abstract:> 本研究は,生物の柔軟な行動を生み出す情報処理システムの本質的原理を化学勾配に基づく数理モデルで表現することを目的とした.単細胞生物の繊毛虫ゾウリムシが障害物に衝突した際の行動応答を生物実験により調べた結果,ゾウリムシは衝突後すぐに方向転換する行動と,障害物に沿って移動した後に方向転換する行動を示した.これらの行動を生じた時の衝突時の角度や速度は同じであったが,直前の角度変化の符号が異なっていた.ゾウリムシの行動は,体表に生えた繊毛運動によって制御され,それは細胞内外の化学勾配に従って生じる膜興奮動態によって調整される.この膜興奮動態と行動とを対応づける数理モデルを構成し,数値シミュレーション実験を行った.その結果,実験結果と同様にゾウリムシが障害物に衝突する前の角度変化の符号の違いで2つの行動を再現できた.つまり,ゾウリムシは同じ化学勾配状態でも,直前の角度変化という運動履歴の違いによって異なる行動を生じる柔軟性を有していた.
<Keywords:> membrane excitation dynamics, chemical gradients, Paramecium, ciliary movement, FitzHugh-Nagumo model
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/advpub/0/advpub_2024-0026/_article/-char/ja/