[Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan -International Edition Vol.7, -, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> Materials Informatics Approach to Predictive Models for Elastic Modulus of Polypropylene Composites Reinforced by Fillers and Additives
<Author(s):> Yuko IKEDA, Michihiro OKUYAMA, Yukihito NAKAZAWA, Tomohiro OSHIYAMA, Kimito FUNATSU
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> tomohiro.oshiyama(at)konicaminolta.com
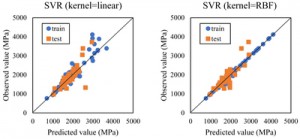
<Abstract:> Advanced processes are useful when developing polymer composites because there are an enormous number of possible combinations of fillers and additives to realize polymers with desired properties. Materials informatics is a data-driven approach to find novel materials or a suitable combination of materials from material data sheets. Here, we used materials informatics to construct a predictive model for the elastic modulus of polypropylene composites. To apply materials informatics to existing experimental data, we described explanatory variables by a combination of 0 and 1 representing polypropylene, or by the content ratio of filler and additive, without using materials property data. We constructed a predictive model for the elastic modulus of polypropylene composites using a partial least square regression model with dummy variables. To validate the predictive model, comparisons were made between measured and predicted elastic moduli for eight new polypropylene composites. The residual was less than 300 MPa for the range 1,000 3,000 MPa. We improved the accuracy of the prediction for composites with high filler content ratio by applying a nonlinear support vector regression model. The predictive model is therefore useful for identifying suitable combinations of polypropylene, filler and additive to achieve a desired elastic modulus.
<Keywords:> Materials informatics, Elastic modulus, Polypropylene composite, PLS, SVR, Dummy variables
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccjie/7/0/7_2020-0007/_html
<Title:> Materials Informatics Approach to Predictive Models for Elastic Modulus of Polypropylene Composites Reinforced by Fillers and Additives
<Author(s):> Yuko IKEDA, Michihiro OKUYAMA, Yukihito NAKAZAWA, Tomohiro OSHIYAMA, Kimito FUNATSU
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> tomohiro.oshiyama(at)konicaminolta.com
<Abstract:> Advanced processes are useful when developing polymer composites because there are an enormous number of possible combinations of fillers and additives to realize polymers with desired properties. Materials informatics is a data-driven approach to find novel materials or a suitable combination of materials from material data sheets. Here, we used materials informatics to construct a predictive model for the elastic modulus of polypropylene composites. To apply materials informatics to existing experimental data, we described explanatory variables by a combination of 0 and 1 representing polypropylene, or by the content ratio of filler and additive, without using materials property data. We constructed a predictive model for the elastic modulus of polypropylene composites using a partial least square regression model with dummy variables. To validate the predictive model, comparisons were made between measured and predicted elastic moduli for eight new polypropylene composites. The residual was less than 300 MPa for the range 1,000 3,000 MPa. We improved the accuracy of the prediction for composites with high filler content ratio by applying a nonlinear support vector regression model. The predictive model is therefore useful for identifying suitable combinations of polypropylene, filler and additive to achieve a desired elastic modulus.
<Keywords:> Materials informatics, Elastic modulus, Polypropylene composite, PLS, SVR, Dummy variables
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccjie/7/0/7_2020-0007/_html