[Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan Vol.21, 123-125, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> 抗体軽鎖四量体の立体構造の理論解析
<Author(s):> Lian Duan, Hengphasatporn Kowit, 重田 育照
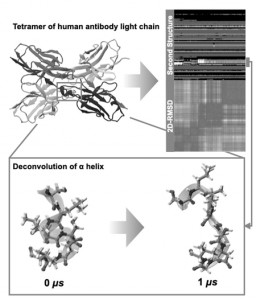
<Abstract:> In this study, the trajectories of the four protomers corresponding to the light chain tetramers of human antibodies were obtained from MD simulations. The four protomers, which should be symmetrically constructed, were not completely symmetrical in the simulations. The DSSP analysis and 2D-RMSD analysis of the four protomers showed that although the secondary structure of the four protomers is approximately the same, the deconvolution of part of the α helix leads to the asymmetry of the overall structure in the simulation. Although the number of interactions within the protomers decreases, that between the protomers increases, making the overall energy more stable. We hypothesize that the deconvolution is caused by the formation of the α helix fragment in the tetramer, and the hydrogen bonding and van der Waals forces between the protomers lead to the breakage of the hydrogen bond within the protomers, further leading to the disappearance of the α helix.
<Keywords:>
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/21/4/21_2023-0005/_article/-char/ja/
<Title:> 抗体軽鎖四量体の立体構造の理論解析
<Author(s):> Lian Duan, Hengphasatporn Kowit, 重田 育照
<Abstract:> In this study, the trajectories of the four protomers corresponding to the light chain tetramers of human antibodies were obtained from MD simulations. The four protomers, which should be symmetrically constructed, were not completely symmetrical in the simulations. The DSSP analysis and 2D-RMSD analysis of the four protomers showed that although the secondary structure of the four protomers is approximately the same, the deconvolution of part of the α helix leads to the asymmetry of the overall structure in the simulation. Although the number of interactions within the protomers decreases, that between the protomers increases, making the overall energy more stable. We hypothesize that the deconvolution is caused by the formation of the α helix fragment in the tetramer, and the hydrogen bonding and van der Waals forces between the protomers lead to the breakage of the hydrogen bond within the protomers, further leading to the disappearance of the α helix.
<Keywords:>
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/21/4/21_2023-0005/_article/-char/ja/