[Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan -International Edition Vol.10, -, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> Dependence of Substituents on UV-vis Spectra and Solvent Effect of Anthocyanins by Quantum Chemical Approach
<Author(s):> Kazuaki KUWAHATA, Yukio KAWASHIMA, Atsushi FUKUSHIMA, Masanori TACHIKAWA, Miyako KUSANO
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> tachi(at)yokohama-cu.ac.jp
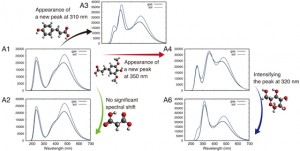
<Abstract:> Plants can produce anthocyanins to survive their given environments. A model plant Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis) accumulates the 11 anthocyanins (A1 A11) with various substitutions to their basic structure. However, it is difficult to detect all 11 anthocyanins in every analysis using conventional analytical techniques. In this study, we predicted ultraviolet visible (UV-vis) absorption spectra of A1 A11 by an ab initio calculation based on density functional theory. We could identify substituents attached to the basic structure of anthocyanins from the predicted absorption peaks. We found that glucose substitution significantly reduced the solvation free energy due to five hydroxyl groups, whereas sinapoyl substitution increased the solvent effect due to the methyl group in a sinapoyl moiety. Our findings may explain the antioxidant capacity of each anthocyanin by comparing the predicted UV-vis absorption spectra with the measured UV-vis spectra. These outcomes can provide clues to uncover anthocyanin biosynthesis in different stress conditions/tissues.
<Keywords:> Anthocyanin, Arabidopsis, Ultraviolet visible absorption, Quantum chemical prediction, Solvent effect.
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccjie/10/0/10_2023-0045/_html
<Title:> Dependence of Substituents on UV-vis Spectra and Solvent Effect of Anthocyanins by Quantum Chemical Approach
<Author(s):> Kazuaki KUWAHATA, Yukio KAWASHIMA, Atsushi FUKUSHIMA, Masanori TACHIKAWA, Miyako KUSANO
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> tachi(at)yokohama-cu.ac.jp
<Abstract:> Plants can produce anthocyanins to survive their given environments. A model plant Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis) accumulates the 11 anthocyanins (A1 A11) with various substitutions to their basic structure. However, it is difficult to detect all 11 anthocyanins in every analysis using conventional analytical techniques. In this study, we predicted ultraviolet visible (UV-vis) absorption spectra of A1 A11 by an ab initio calculation based on density functional theory. We could identify substituents attached to the basic structure of anthocyanins from the predicted absorption peaks. We found that glucose substitution significantly reduced the solvation free energy due to five hydroxyl groups, whereas sinapoyl substitution increased the solvent effect due to the methyl group in a sinapoyl moiety. Our findings may explain the antioxidant capacity of each anthocyanin by comparing the predicted UV-vis absorption spectra with the measured UV-vis spectra. These outcomes can provide clues to uncover anthocyanin biosynthesis in different stress conditions/tissues.
<Keywords:> Anthocyanin, Arabidopsis, Ultraviolet visible absorption, Quantum chemical prediction, Solvent effect.
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccjie/10/0/10_2023-0045/_html