[Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan Vol.23, 68-70, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> 実時間TDDFTの時系列データに関する特異スペクトル解析
<Author(s):> 谷 直樹, 狩野 覚, 善甫 康成
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> naoki.tani.7x(at)stu.hosei.ac.jp
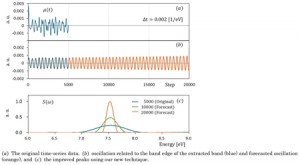
<Abstract:> Optical spectrum prediction based on first-principles calculations is important for the development of optical materials. In particular, Time Dependent Density Functional Theory (TDDFT) in real-time is one of the most widely used calculation methods. In real-time TDDFT, the dynamic dipole moment is used to obtain the polarizability by Fourier transform (FT). The optical spectrum can be obtained from this polarizability. However, if the time length is not sufficient, the spectrum becomes ambiguous. To solve this problem, we introduced singular spectrum analysis (SSA), which decomposes time series data into multiple orthogonal oscillations. By extracting only the main components related to the peak of interest, the corresponding time series data is reproduced. In this process, high-frequency oscillations recognized as noise are removed. We applied this method to TDDFT time-series data for ethylene and small molecules of benzene, naphthalene, anthracene and tetracene. We focused on band edges, which are important for understanding optical properties, to clarify the signals. Even when the time-series data is insufficient, we found that it is possible to obtain time-series data of sufficient time length by isolating the oscillation components contributing to the band edges and expanding and complementing them with time-series prediction.
<Keywords:> Keywords TDDFT, Singular Spectrum Analysis (SSA), Fourier Transform (FT)
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/23/3/23_2024-0021/_article/-char/ja/
<Title:> 実時間TDDFTの時系列データに関する特異スペクトル解析
<Author(s):> 谷 直樹, 狩野 覚, 善甫 康成
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> naoki.tani.7x(at)stu.hosei.ac.jp
<Abstract:> Optical spectrum prediction based on first-principles calculations is important for the development of optical materials. In particular, Time Dependent Density Functional Theory (TDDFT) in real-time is one of the most widely used calculation methods. In real-time TDDFT, the dynamic dipole moment is used to obtain the polarizability by Fourier transform (FT). The optical spectrum can be obtained from this polarizability. However, if the time length is not sufficient, the spectrum becomes ambiguous. To solve this problem, we introduced singular spectrum analysis (SSA), which decomposes time series data into multiple orthogonal oscillations. By extracting only the main components related to the peak of interest, the corresponding time series data is reproduced. In this process, high-frequency oscillations recognized as noise are removed. We applied this method to TDDFT time-series data for ethylene and small molecules of benzene, naphthalene, anthracene and tetracene. We focused on band edges, which are important for understanding optical properties, to clarify the signals. Even when the time-series data is insufficient, we found that it is possible to obtain time-series data of sufficient time length by isolating the oscillation components contributing to the band edges and expanding and complementing them with time-series prediction.
<Keywords:> Keywords TDDFT, Singular Spectrum Analysis (SSA), Fourier Transform (FT)
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/23/3/23_2024-0021/_article/-char/ja/