[Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan Vol.17, 160-162, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> FMO法によるエストロゲン受容体のリガンド結合特異性解析
<Author(s):> 関 祐哉, 加藤 司, 古石 誉之, 福澤 薫, 米持 悦生
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> k-fukuzawa(at)hoshi.ac.jp
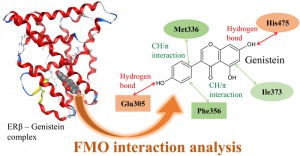
<Abstract:> There are two subtypes (α, β) in the estrogen receptor (ER), and ERβ has binding selectivity for phytoestrogens. It is known that only two hydrophobic amino acid residues (Met336Leu and Ile373Met) differ in ligand binding pocket between subtypes. However, the mechanisms of its binding properties and subtype selectivity have not been fully understood. We evaluated the subtype selectivity by comprehensively analyzing the complex of ERβ and ligands based on the fragment molecular orbital (FMO) method. By comparing the interaction between ligand and amino acid residues of ER, it was revealed that both hydrogen bond with Glu305 and CH/π interaction with Phe356 were essential for ligand binding of ERβ, and stable interaction with Met336 and His475 would be related to β selectivity.
<Keywords:> Estrogen Receptor β, Fragment Molecular Orbital Method, PIEDA, Protein-Ligand Interaction, Subtype Selectivity
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/17/3/17_2018-0028/_article/-char/ja/