[Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan Vol.18, 164-165, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> フォルステライトガラス表面における水分子の分解メカニズム
<Author(s):> 久保 文音, 西澤 隼哉, 深澤 倫子
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> fukazawa(at)meiji.ac.jp
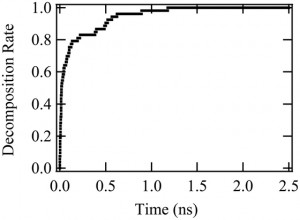
<Abstract:> To investigate the decomposition mechanisms of adsorbed H2O molecules as a monolayer on the surface of forsterite glass, we performed molecular dynamics calculations. The decomposition phenomenon of H2O molecules is observed at temperatures above 200 K. The equilibrium rate of the decomposed H2O increases as the temperature increases and approaches 1.0 at temperatures above 500 K. The decomposed hydrogen forms MgOxHy or SiO4Hz structures with MgOx or SiOz units in forsterite glass. The processes of decomposition and reformation of the structure units on the surface of forsterite glass have important implications for chemical evolution in interstellar spaces.
<Keywords:> Molecular dynamics calculation, Forsterite glass, Amorphous ice, Surface
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/18/3/18_2019-0017/_article/-char/ja/