[Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan Vol.21, 48-51, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> COVID-19の経口治療薬開発に向けたハイブリッド型in Silico創薬
<Author(s):> 小清水 初花, 小野 純一, 福西 快文, 中井 浩巳
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> nakai(at)waseda.jp
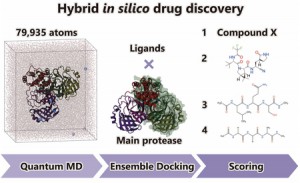
<Abstract:> Hybrid in silico drug discovery was performed by combining large-scale quantum molecular dynamics (QMD) simulations with the conventional in silico drug discovery, focusing on developing covalent inhibitors against the main protease (Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The crystal structures and instantaneous structures obtained from the large-scale QMD simulations for Mpro were used as receptors in ensemble docking to estimate the binding affinities of the four ligands: the natural substrate recognized by Mpro, that recognized by the other enzyme of SARS-CoV-2, approved covalent inhibitor (PF-07321332), and the new candidate compound X determined from virtual screening. The present result shows that the binding affinity of X was comparable to that of PF-07321332, demonstrating the potency of our drug discovery.
<Keywords:> COVID-19, In silico drug discovery, Quantum molecular dynamics, Main protease, Covalent drug
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/21/2/21_2022-0029/_article/-char/ja/
<Title:> COVID-19の経口治療薬開発に向けたハイブリッド型in Silico創薬
<Author(s):> 小清水 初花, 小野 純一, 福西 快文, 中井 浩巳
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> nakai(at)waseda.jp
<Abstract:> Hybrid in silico drug discovery was performed by combining large-scale quantum molecular dynamics (QMD) simulations with the conventional in silico drug discovery, focusing on developing covalent inhibitors against the main protease (Mpro) of SARS-CoV-2, the virus responsible for ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The crystal structures and instantaneous structures obtained from the large-scale QMD simulations for Mpro were used as receptors in ensemble docking to estimate the binding affinities of the four ligands: the natural substrate recognized by Mpro, that recognized by the other enzyme of SARS-CoV-2, approved covalent inhibitor (PF-07321332), and the new candidate compound X determined from virtual screening. The present result shows that the binding affinity of X was comparable to that of PF-07321332, demonstrating the potency of our drug discovery.
<Keywords:> COVID-19, In silico drug discovery, Quantum molecular dynamics, Main protease, Covalent drug
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/21/2/21_2022-0029/_article/-char/ja/