[Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan Vol.23, 62-64, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> 動的分極率を用いた励起状態計算における励起配置解析
<Author(s):> 西村 龍星, 吉川 武司, 坂田 健, 中井 浩巳
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> nakai(at)waseda.jp
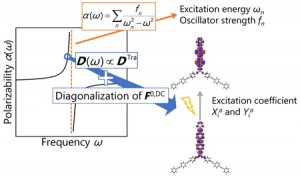
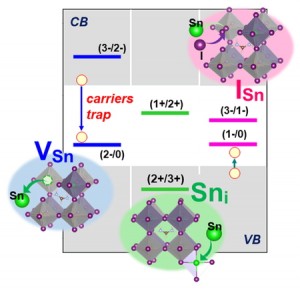
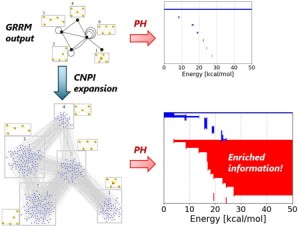
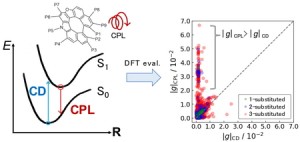
<Abstract:> We previously proposed an excitation configuration analysis for the divide-and-conquer (DC)-based excited-state calculation method using dynamical polarizability to interpret the nature of excited states [J. Chem. Phys. 160, 244103 (2024)]. This article reviews the proposed DC-based excitation configuration analysis and applies the natural transition orbital analysis based on the (de-)excitation coefficients obtained from the proposed method to the lowest excited state of tris-triphenylacetylammonia. The singular values of excitation coefficients were matched to the results of the TDHF method. Also, the shapes of the natural transition orbitals coincided as well.
<Keywords:> Excited-state calculation, Time-dependent Hartree Fock/density functional theory, Divide-and-conquer, Dynamical polarizability
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/23/3/23_2024-0027/_article/-char/ja/
<Title:> 動的分極率を用いた励起状態計算における励起配置解析
<Author(s):> 西村 龍星, 吉川 武司, 坂田 健, 中井 浩巳
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> nakai(at)waseda.jp
<Abstract:> We previously proposed an excitation configuration analysis for the divide-and-conquer (DC)-based excited-state calculation method using dynamical polarizability to interpret the nature of excited states [J. Chem. Phys. 160, 244103 (2024)]. This article reviews the proposed DC-based excitation configuration analysis and applies the natural transition orbital analysis based on the (de-)excitation coefficients obtained from the proposed method to the lowest excited state of tris-triphenylacetylammonia. The singular values of excitation coefficients were matched to the results of the TDHF method. Also, the shapes of the natural transition orbitals coincided as well.
<Keywords:> Excited-state calculation, Time-dependent Hartree Fock/density functional theory, Divide-and-conquer, Dynamical polarizability
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/23/3/23_2024-0027/_article/-char/ja/