[Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan Vol.24, 20-26, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> Anion Intercalation and Selectivity in NiFe LDH: Insights from Neural Network-Enhanced Molecular Dynamics
<Author(s):> Tien Quang NGUYEN, Susan Me ez ASPERA, Yingjie CHEN, Kaoru HISAMA, Michihisa KOYAMA
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> quang(at)shinshu-u.ac.jp
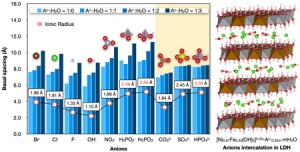
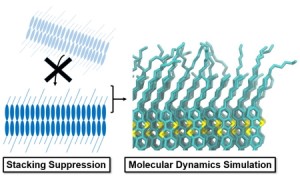
<Abstract:> Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, accelerated by a universal neural network potential, were employed to investigate the dynamic behaviors of ten inorganic anions (Br–, Cl–, F–, OH–, NO3–, H2PO2–, H2PO3–, HPO42-, CO32- and SO42-) intercalated into NiFe layered double hydroxide at varying hydration levels. Our results show that the lattice parameters along the layered double hydroxide (LDH) layers are minimally affected by the intercalated anions and water content, while the lattice parameter perpendicular to the layers, i.e., the basal spacing, is strongly influenced by the type of anion and hydration level. The basal spacing is closely correlated with the ionic radius and charge of the anions, as well as the amount of water uptake. Mean squared displacement (MSD) analysis reveals distinct behaviors of the anions under different hydration conditions. While some anions, such as NO3– and H2PO2–, exhibit noticeable mobility, others remain largely immobilized, primarily due to strong electrostatic interactions with the LDH layers and water molecules. Hydration weakens the interaction between anions and the LDH but also restricts the mobility of anions due to the formation of hydration shells. These findings provide insights into anion dynamics and selectivity in NiFe LDH, which are critical for designing materials for anion removal applications.
<Keywords:> Layered-double hydroxides, Anion intercalation, Molecular dynamics, Neural network potential, Coulomb interactions
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/24/1/24_2025-0001/_article/-char/ja/
<Title:> Anion Intercalation and Selectivity in NiFe LDH: Insights from Neural Network-Enhanced Molecular Dynamics
<Author(s):> Tien Quang NGUYEN, Susan Me ez ASPERA, Yingjie CHEN, Kaoru HISAMA, Michihisa KOYAMA
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> quang(at)shinshu-u.ac.jp
<Abstract:> Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, accelerated by a universal neural network potential, were employed to investigate the dynamic behaviors of ten inorganic anions (Br–, Cl–, F–, OH–, NO3–, H2PO2–, H2PO3–, HPO42-, CO32- and SO42-) intercalated into NiFe layered double hydroxide at varying hydration levels. Our results show that the lattice parameters along the layered double hydroxide (LDH) layers are minimally affected by the intercalated anions and water content, while the lattice parameter perpendicular to the layers, i.e., the basal spacing, is strongly influenced by the type of anion and hydration level. The basal spacing is closely correlated with the ionic radius and charge of the anions, as well as the amount of water uptake. Mean squared displacement (MSD) analysis reveals distinct behaviors of the anions under different hydration conditions. While some anions, such as NO3– and H2PO2–, exhibit noticeable mobility, others remain largely immobilized, primarily due to strong electrostatic interactions with the LDH layers and water molecules. Hydration weakens the interaction between anions and the LDH but also restricts the mobility of anions due to the formation of hydration shells. These findings provide insights into anion dynamics and selectivity in NiFe LDH, which are critical for designing materials for anion removal applications.
<Keywords:> Layered-double hydroxides, Anion intercalation, Molecular dynamics, Neural network potential, Coulomb interactions
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/24/1/24_2025-0001/_article/-char/ja/