[Advanced Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> First-Principles Calculations of Stability, Electronic Structure, and Sorption Properties of Nanoparticle Systems
<Author(s):> Gerardo VALADEZ HUERTA, Yusuke NANBA, Nor Diana Binti ZULKIFLI, David Samuel RIVERA ROCABADO, Takayoshi ISHIMOTO, Michihisa KOYAMA
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> koyama_michihisa(at)shinshu-u.ac.jp
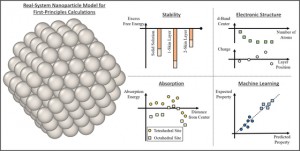
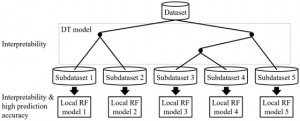
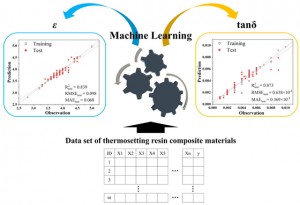
<Abstract:> Nanoparticles have a wide range of applications as catalysts. Their catalytic and electronic properties differ from those of materials with flat surfaces and bulk materials. First-principles calculations of real system nanoparticles, which use nanoparticle models based on real shapes extracted from experimental observations, are essential for studying these properties to facilitate the computational design of new catalysts. In this article, we review first-principles studies of models of real systems of monometallic, bimetallic, and supported nanoparticles. The stability, electronic structure, hydrogen absorption behavior, and small molecule adsorption behavior are reviewed, and advances in first-principles calculations of real system nanoparticles are presented. Further, a combination of machine learning and first-principles studies is also considered. Future perspectives are discussed on the basis of these examples.
<Keywords:> Density functional theory, Real system structure, Nanoparticle, Machine learning
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/advpub/0/advpub_2021-0028/_article/-char/ja/
<Title:> First-Principles Calculations of Stability, Electronic Structure, and Sorption Properties of Nanoparticle Systems
<Author(s):> Gerardo VALADEZ HUERTA, Yusuke NANBA, Nor Diana Binti ZULKIFLI, David Samuel RIVERA ROCABADO, Takayoshi ISHIMOTO, Michihisa KOYAMA
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> koyama_michihisa(at)shinshu-u.ac.jp
<Abstract:> Nanoparticles have a wide range of applications as catalysts. Their catalytic and electronic properties differ from those of materials with flat surfaces and bulk materials. First-principles calculations of real system nanoparticles, which use nanoparticle models based on real shapes extracted from experimental observations, are essential for studying these properties to facilitate the computational design of new catalysts. In this article, we review first-principles studies of models of real systems of monometallic, bimetallic, and supported nanoparticles. The stability, electronic structure, hydrogen absorption behavior, and small molecule adsorption behavior are reviewed, and advances in first-principles calculations of real system nanoparticles are presented. Further, a combination of machine learning and first-principles studies is also considered. Future perspectives are discussed on the basis of these examples.
<Keywords:> Density functional theory, Real system structure, Nanoparticle, Machine learning
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/advpub/0/advpub_2021-0028/_article/-char/ja/