[Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan -International Edition Vol.7, -, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> Development of a Protein-Gene Motif Dictionary System for One-Stop Motif Analysis
<Author(s):> Masahiro OHTOMO, Hiroaki KATO
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> ohtomo(at)kuicr.kyoto-u.ac.jp
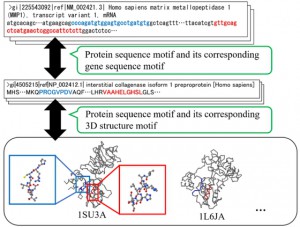
<Abstract:> The amino acid sequence of a protein is closely related to its structure and function. This is especially true for particular structural features called motifs, which are well-reserved sites in genome sequences. Biological data, such as the data for biopolymers, are rapidly increasing. Constructing a database for efficient analysis is important for identifying the structure and function of unknown biological data. Here, we constructed a protein-gene motif dictionary system for several model species using NoSQL, a database management system. This dictionary stored protein sequence motifs based on PROSITE, along with their corresponding mRNA sequences. Additionally, the database stored 3D structural information of the corresponding protein sequence motifs. The protein-gene dictionary has 49,265 registered entries, 120,047 sequence motifs, and 57,452 3D structural motifs from 7 model species. Software tools with graphical user interface were also developed to assist with intuitive search and analysis using the system. As a result, we discovered that zinc protease motif had co-occurrence with the cysteine switch motif. It was followed by the cysteine switch motif with a gap of 117 to 293 amino acids, however, its 3D Euclidean distance was preserved at around 12 .
<Keywords:> Protein motif, Nucleotide motif, Protein-gene motif dictionary, 3D structural motif, PROSITE, Co-occurrence motif analysis
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccjie/7/0/7_2020-0008/_html
<Title:> Development of a Protein-Gene Motif Dictionary System for One-Stop Motif Analysis
<Author(s):> Masahiro OHTOMO, Hiroaki KATO
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> ohtomo(at)kuicr.kyoto-u.ac.jp
<Abstract:> The amino acid sequence of a protein is closely related to its structure and function. This is especially true for particular structural features called motifs, which are well-reserved sites in genome sequences. Biological data, such as the data for biopolymers, are rapidly increasing. Constructing a database for efficient analysis is important for identifying the structure and function of unknown biological data. Here, we constructed a protein-gene motif dictionary system for several model species using NoSQL, a database management system. This dictionary stored protein sequence motifs based on PROSITE, along with their corresponding mRNA sequences. Additionally, the database stored 3D structural information of the corresponding protein sequence motifs. The protein-gene dictionary has 49,265 registered entries, 120,047 sequence motifs, and 57,452 3D structural motifs from 7 model species. Software tools with graphical user interface were also developed to assist with intuitive search and analysis using the system. As a result, we discovered that zinc protease motif had co-occurrence with the cysteine switch motif. It was followed by the cysteine switch motif with a gap of 117 to 293 amino acids, however, its 3D Euclidean distance was preserved at around 12 .
<Keywords:> Protein motif, Nucleotide motif, Protein-gene motif dictionary, 3D structural motif, PROSITE, Co-occurrence motif analysis
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccjie/7/0/7_2020-0008/_html