[Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan Vol.24, 27-29, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> PdおよびAgRh合金ナノクラスターへの水素吸収と拡散に関する相対論的量子化学計算分子動力学シミュレーション
<Author(s):> 木村 愛花, 安藤 耕司
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> ando_k(at)lab.twcu.ac.jp
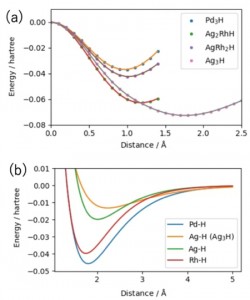
<Abstract:> Molecular dynamics simulations of hydrogen absorption and diffusion in Pd and AgRh alloy nanoclusters were performed. Parameters for atomic interaction potentials were determined from relativistic quantum chemical calculations. Although Rh is known not to absorb hydrogen in bulk, the Rh-H interaction strength obtained from the calculations was about 80% of that of the Pd-H. Using the parameters obtained, molecular dynamics simulations were performed. Molecular dynamics simulations of AgRh clusters with different Ag:Rh ratio have shown no significant difference in the Rh-Rh distance distribution at the nearest neighbor except for Ag70Rh30. However, at the second nearest neighbor the distance increased as the Ag fraction increased.
<Keywords:> Keywords Molecular dynamics simulation, Relativistic Quantum Chemical Calculations, Hydrogen-absorbing metal nanoclusters
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/24/1/24_2024-0040/_article/-char/ja/
<Title:> PdおよびAgRh合金ナノクラスターへの水素吸収と拡散に関する相対論的量子化学計算分子動力学シミュレーション
<Author(s):> 木村 愛花, 安藤 耕司
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> ando_k(at)lab.twcu.ac.jp
<Abstract:> Molecular dynamics simulations of hydrogen absorption and diffusion in Pd and AgRh alloy nanoclusters were performed. Parameters for atomic interaction potentials were determined from relativistic quantum chemical calculations. Although Rh is known not to absorb hydrogen in bulk, the Rh-H interaction strength obtained from the calculations was about 80% of that of the Pd-H. Using the parameters obtained, molecular dynamics simulations were performed. Molecular dynamics simulations of AgRh clusters with different Ag:Rh ratio have shown no significant difference in the Rh-Rh distance distribution at the nearest neighbor except for Ag70Rh30. However, at the second nearest neighbor the distance increased as the Ag fraction increased.
<Keywords:> Keywords Molecular dynamics simulation, Relativistic Quantum Chemical Calculations, Hydrogen-absorbing metal nanoclusters
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/24/1/24_2024-0040/_article/-char/ja/