[Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan Vol.21, 129-133, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> 汎用ニューラルネットワークポテンシャルを用いた 三元系ナノ合金のCO吸着特性の評価
<Author(s):> 綾子 田村, Gerardo VALADEZ HUERTA, 優輔 難波, 馨 久間, 通久 古山
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> ayako_tamura(at)shinshu-u.ac.jp
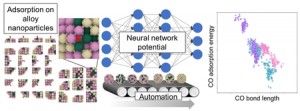
<Abstract:> Multi-element alloy nanoparticles have attracted attention for their potentially high catalytic properties. However, a high degree of freedom in configurations of metal atoms within nanoparticle increases the distinct adsorption sites, making it difficult to theoretically analyze its catalytic properties because the first-principles calculation requires a considerable computational cost. In this study, we develop a sequential scheme to calculate hundreds of adsorption sites by employing a pre-trained universal neural network potential named PFP. Our automated scheme is applied to CO single-molecule adsorption of CO onto PtRuIr ternary alloy nanoparticles. The calculation results are first compared with DFT results to confirm the accuracy. Adsorption energies in the alloy systems are widely distributed in comparison with those of the monometal counterparts, indicating that the alloy nanoparticle includes adsorption sites with various catalytic activities.
<Keywords:> Alloy nanoparticle, Universal neural network potential, CO adsorption
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/21/4/21_2023-0016/_article/-char/ja/
<Title:> 汎用ニューラルネットワークポテンシャルを用いた 三元系ナノ合金のCO吸着特性の評価
<Author(s):> 綾子 田村, Gerardo VALADEZ HUERTA, 優輔 難波, 馨 久間, 通久 古山
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> ayako_tamura(at)shinshu-u.ac.jp
<Abstract:> Multi-element alloy nanoparticles have attracted attention for their potentially high catalytic properties. However, a high degree of freedom in configurations of metal atoms within nanoparticle increases the distinct adsorption sites, making it difficult to theoretically analyze its catalytic properties because the first-principles calculation requires a considerable computational cost. In this study, we develop a sequential scheme to calculate hundreds of adsorption sites by employing a pre-trained universal neural network potential named PFP. Our automated scheme is applied to CO single-molecule adsorption of CO onto PtRuIr ternary alloy nanoparticles. The calculation results are first compared with DFT results to confirm the accuracy. Adsorption energies in the alloy systems are widely distributed in comparison with those of the monometal counterparts, indicating that the alloy nanoparticle includes adsorption sites with various catalytic activities.
<Keywords:> Alloy nanoparticle, Universal neural network potential, CO adsorption
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/21/4/21_2023-0016/_article/-char/ja/