[Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan Vol.22, 18-20, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> Theoretical Analysis of the Aggregation-Inhibition Effect of Arginine on Polyglutamine Protein by the Generalized-Ensemble Method
<Author(s):> Shoichi TANIMOTO, Hisashi OKUMURA
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> sktanimoto(at)ims.ac.jp
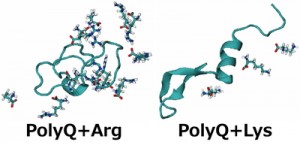
<Abstract:> The aggregation of polyglutamine (polyQ) proteins, which have the abnormal expansion of glutamine repeats, is a critical pathological hallmark of polyQ diseases. Experimental studies have shown an amino acid arginine uniquely inhibits the polyQ-protein aggregation. We performed replica-permutation molecular dynamics simulations to clarify the inhibitory effects of arginine on the polyQ-protein aggregation. We found arginine makes more contact with the polyQ protein than lysine, and this tendency of arginine likely inhibits the polyQ-protein aggregation.
<Keywords:> Molecular dynamics simulation, Generalized-ensemble algorithm, Polyglutamine, Protein-aggregation inhibition, Amyloid
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/22/2/22_2023-0020/_article/-char/ja/
<Title:> Theoretical Analysis of the Aggregation-Inhibition Effect of Arginine on Polyglutamine Protein by the Generalized-Ensemble Method
<Author(s):> Shoichi TANIMOTO, Hisashi OKUMURA
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> sktanimoto(at)ims.ac.jp
<Abstract:> The aggregation of polyglutamine (polyQ) proteins, which have the abnormal expansion of glutamine repeats, is a critical pathological hallmark of polyQ diseases. Experimental studies have shown an amino acid arginine uniquely inhibits the polyQ-protein aggregation. We performed replica-permutation molecular dynamics simulations to clarify the inhibitory effects of arginine on the polyQ-protein aggregation. We found arginine makes more contact with the polyQ protein than lysine, and this tendency of arginine likely inhibits the polyQ-protein aggregation.
<Keywords:> Molecular dynamics simulation, Generalized-ensemble algorithm, Polyglutamine, Protein-aggregation inhibition, Amyloid
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccj/22/2/22_2023-0020/_article/-char/ja/