[Published online Journal of Computer Chemistry, Japan -International Edition Vol.3, -, by J-STAGE]
<Title:> Practical Training on Adding Polarization Function to Basis Set for Molecular Orbital Calculation of Ethylene
<Author(s):> Shin-ichi NAGAOKA, Hiroyuki TERAMAE, Umpei NAGASHIMA
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> nagaoka(at)ehime-u.ac.jp
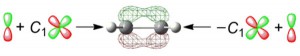
<Abstract:> Adding a polarization function to a basis set for molecular orbital calculation is frequently useful for producing accurate representations of chemical bonding. This article explains practical training that could greatly promote intuitive understanding of the general idea of adding a 3d-type polarization function in a π-type molecular-orbital function. In the training, by using Microsoft Excel, students draw contour plots of the molecular orbitals supplemented with and without the polarization function in ethylene (CH2 = CH2), and visualize the effect of the addition.
<Keywords:> Orbital contour plot, Polarization function, Ethylene, C2H4, Chemical Education
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccjie/3/0/3_2016-0068/_html
<Title:> Practical Training on Adding Polarization Function to Basis Set for Molecular Orbital Calculation of Ethylene
<Author(s):> Shin-ichi NAGAOKA, Hiroyuki TERAMAE, Umpei NAGASHIMA
<Corresponding author E-Mill:> nagaoka(at)ehime-u.ac.jp
<Abstract:> Adding a polarization function to a basis set for molecular orbital calculation is frequently useful for producing accurate representations of chemical bonding. This article explains practical training that could greatly promote intuitive understanding of the general idea of adding a 3d-type polarization function in a π-type molecular-orbital function. In the training, by using Microsoft Excel, students draw contour plots of the molecular orbitals supplemented with and without the polarization function in ethylene (CH2 = CH2), and visualize the effect of the addition.
<Keywords:> Orbital contour plot, Polarization function, Ethylene, C2H4, Chemical Education
<URL:> https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jccjie/3/0/3_2016-0068/_html